Research Projects
Overview of Our Works and Contributions
Hardware/Algorithm Co-optimization for Homomorphic Encryption
-
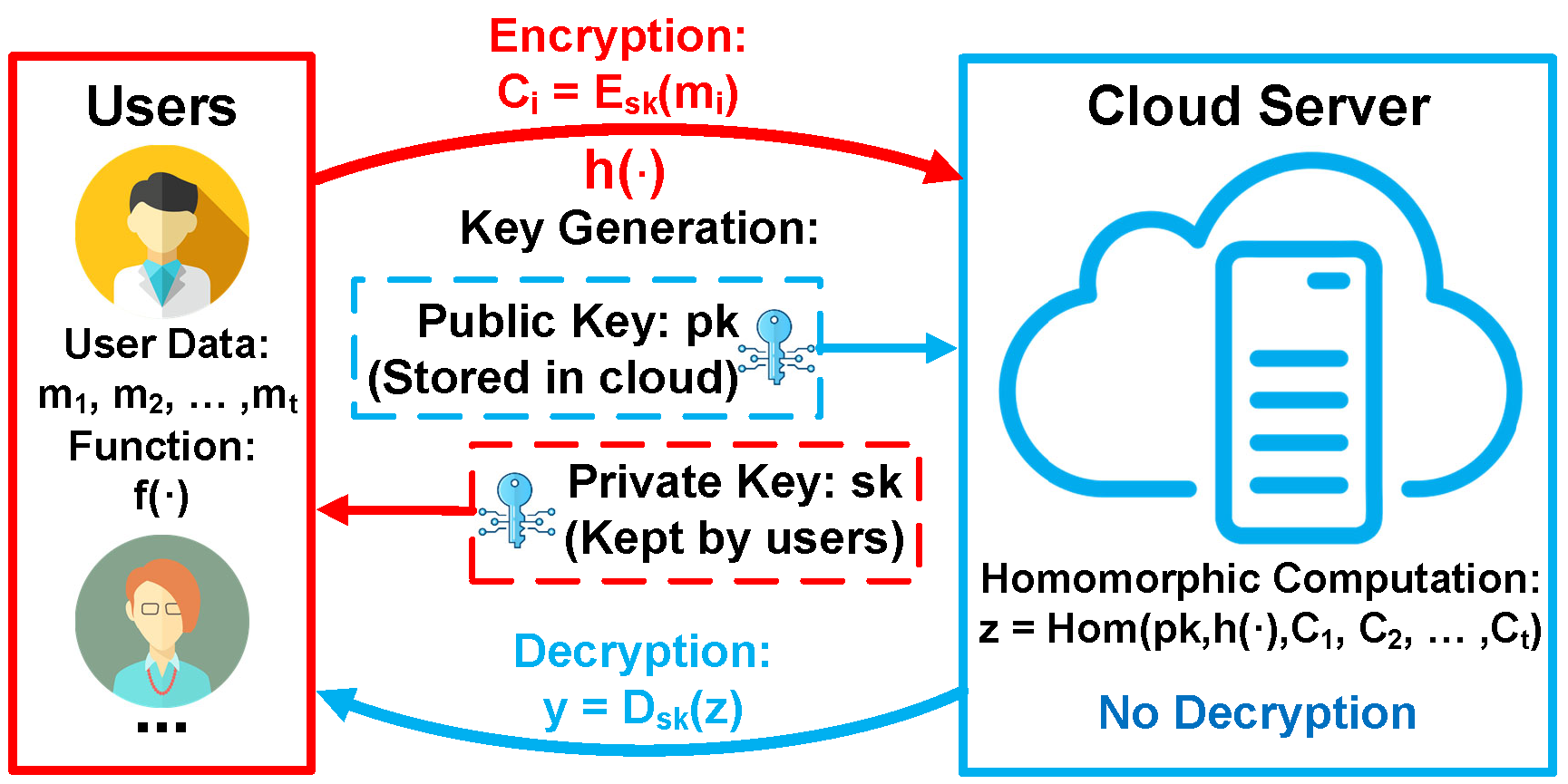
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) represents a data security technique that ensures the encrypted status of data through mathematical confirmation, offering an unprecedented degree of assurance about the storage and handling of data. In contrast to conventional encryption methods that only safeguard data during storage or transmission, requiring decryption for computations, analyses, or utilization in machine learning models, FHE stands out. The need for decryption often places the data at risk of being accessed by skilled opponents or inadvertently leaked. However, FHE permits computations to be executed on the encrypted data itself, creating an equilibrium between maximizing the use of sensitive data and minimizing the chance of unauthorized disclosure.
- Project 1: Hardware/Algorithm Co-optimization for HE
- Project 2: Efficient and Scalable Privacy-Preserving Neural Network Inference based on Ciphertext-Ciphertext Fully Homomorphic Encryption
Some publications include IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, Journal of Signal Processing Systems, etc.
Please refer to Useful resource for homomorphic encryption for more detail.
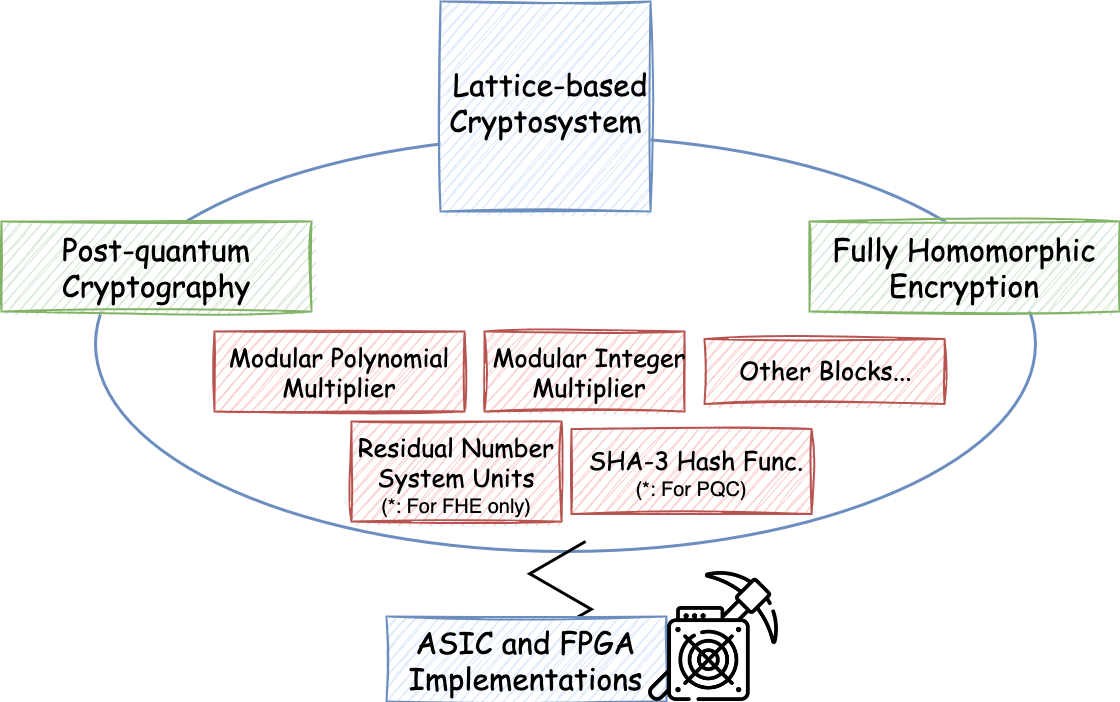
Hardware Acceleration for Lattice-based Post-quantum Cryptography

Post-quantum cryptography, also referred to as quantum-resistant cryptography, involves creating cryptographic algorithms that are secure against both conventional and potential future quantum computers. Quantum computers, which utilize quantum mechanics, could solve mathematical problems that are currently intractable, potentially breaking existing public-key cryptosystems. The advent of such technology could compromise the security of digital communications globally. To preempt this, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standardized the quantum-resistant algorithms: Module-Lattice-Based Key-Encapsulation Mechanism Standard (derived from the CRYSTALS-KYBER), Module-Lattice-Based Digital Signature Standard, and Stateless Hash-Based Digital Signature Standard (See Three Draft FIPS for Post-Quantum Cryptography by NIST). As deploying new cryptographic infrastructure takes significant time, this proactive action is essential for future-proofing our information security systems. More information and latest news: NIST to Standardize Encryption Algorithms That Can Resist Attack by Quantum Computers.
Some publications include IEEE Transactions on Computers (optimization for Saber scheme), IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD) (optimization for CRYSTALS-KYBER or ML-KEM scheme), Asian Hardware Oriented Security and Trust Symposium (AsianHOST) (optimization for NewHope scheme), etc.
